
Dairy alternatives: Lactose-free products, almond, oat, or soy alternatives. Fish: Crab, lobster, salmon, shrimp, tuna. Recent advancements in the dietary management of IBS highlighting the use of a patient-centered, personalized nutrition approach along with lifestyle changes, pharmacological therapies, and psychosocial and behavioral interventions are also reviewed and discussed. To ease symptoms of bloating and gas, try to avoid gassy foods such as beans, Brussels sprouts, wheat germ, raisins, and celery. Protein: Beef, chicken, eggs, tofu, turkey.

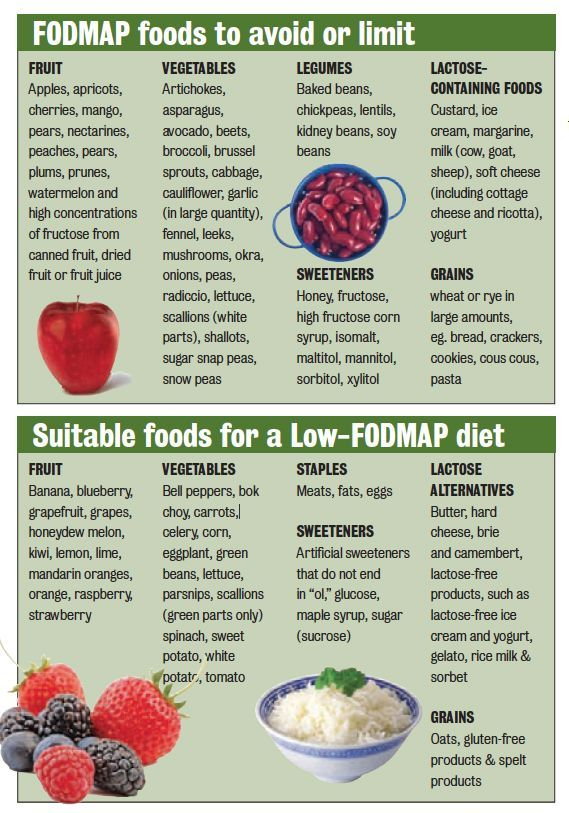
The clinical practice guidelines recommended by the American College of Gastroenterology outlines evidence-based dietary recommendations for patients with IBS to manage symptoms. The American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guidelines for. Some of the diets that are discussed in this article include a low-FODMAP (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols) diet, gluten-free/wheat-free diet, high-fiber diet, dietary and herbal supplements (psyllium, peppermint oil), and probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics. The most popular diet treatment for IBS is a finely tuned menu of low-fermentable foods. This diet is designed to help people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and/or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) figure out which foods are problematic and which foods reduce symptoms. There is no single dietary recommendation for IBS, because everyone experiences symptoms differently, and different foods may trigger symptoms for different. Whereas there are various management approaches cited in the literature to manage symptoms of IBS, the purpose of this article is to focus on dietary options that will restore the gut microbiome and help in managing IBS symptoms. Phase 2: This is the reintroduction phase, lasting 610 weeks. It typically involves eliminating as many high-FODMAP foods as possible to see if symptoms improve. Phase 1: This is the FODMAP restriction phase, which can last 48 weeks. The structure and function of gut microbiota are affected by genetics and environmental factors, such as altered dietary habits, gastroenteritis, stress, increased use of alcohol and drugs, and medication use. The FODMAP diet for IBS follows a three-phase pattern. A healthy diet plays an integral role in maintaining the gut microbiota equilibrium, thus promoting digestive health.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder leading to chronic debilitating issues.

Dietary Modification for the Restoration of Gut Microbiome and Management of Symptoms in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a medical disorder with symptoms including gas, bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea or constipation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
